Workshop Description
Learn the fundamentals of the Ansible Automation platform by utilizing it in an applied fashion. As part of the workshop, you will introduced to general concepts of Ansible, pick up some principles of running Ansible adhoc commands and generating playbooks, work with the Ansible Automation platform (running on Red Hat OpenShift); while, deploying a working containerized edge solution.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is a simple open source universal automation languague (written in YAML) utilized by IT systems teams to automate IT services (provision, configure, manage, and deploy).
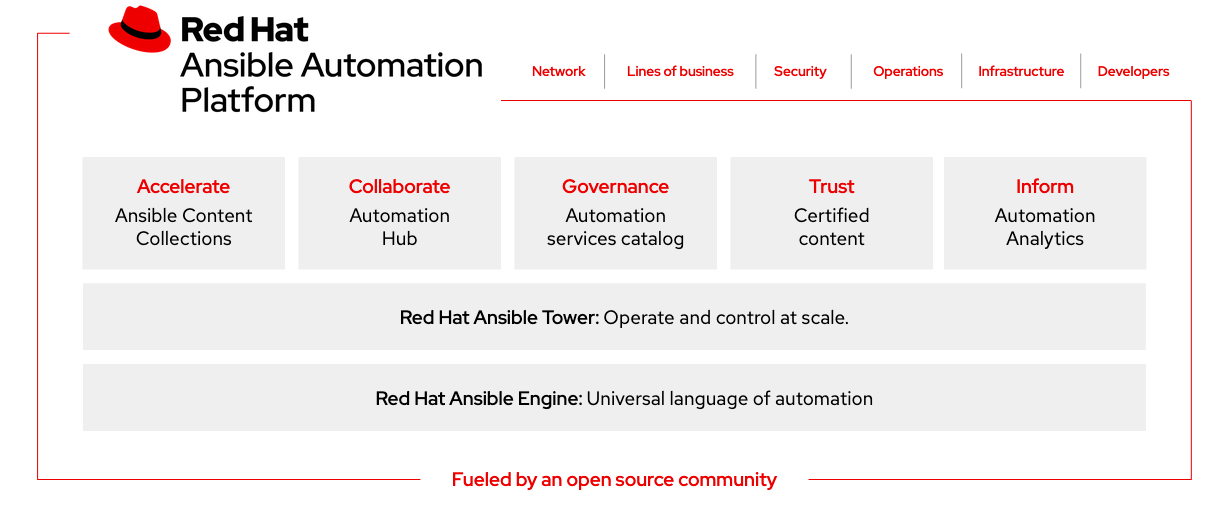
What is Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform?
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is a foundation for building and operating automation services at scale using Ansible … providing enterprises a composable, collaborative, and trusted execution environment.
Ansible Automation Platform allows users to take three simple actions with their enterprise automation journey:
-
Create: Get started faster by combining the power of Ansible’s massive open source community and prebuilt Content Collections of the most-used Ansible roles and modules. Codify your infrastructure and share across teams and individuals where you are already running deployments, whether on-premise or in the cloud.
-
Scale: Easily transfer your automation into multiple domains and across different use cases. Stakeholders across developer, operator, and line-of-business teams can now engage with Ansible in ways that work best for them and make sense for their individual roles without slowing development time.
-
Engage: Take your automation even further with analytics, policy and governance, and content management. These tools in Ansible Automation Platform make day-to-day life more efficient, allowing you to solve problems once and share the results with everyone.
Red Hat Ansible Automation is composed of several components:
-
Ansible Engine is the simplest way to automate your IT infrastructure. The Ansible task engine is a commland line tool that is powered by massive, global community behind the Ansible project. The engine utilize connection transports (SSH, WinRM, REST, etc.) to connect to hosts, nodes, end-points, network devices, storage devices, clouds, virtualization engines, and more and executes automation based on routines defined via the Ansible language. Ansible allows organizations a starting point to develop Infrastructure-as-Code for their deployments.
-
Ansible Tower is a web-based solution that makes Ansible even more easy to use for IT teams of all kinds. It’s designed to be the hub for all of your automation tasks and is the enterprise foundation of the Ansible Automation Platform. Ansible Tower allows users to centralize and control their IT infrastructure with a visual dashboard, role-based access control, API controls, and more.
-
Content Collections makes it easier for Ansible users to get up and running with precomposed Ansible functions (known as roles and/or modules). This prepackaged Ansible content is sorted by content domain and is backed by a robust partner network of certified modules, all requiring less upfront work by the customer to seek and assemble different roles and modules.
-
Automation Hub is the official location to discover and understand Red Hat-supported Ansible content and Ansible Certified Partner content. This portal lets users get started faster with Ansible, find precomposed content written by Ansible Certified Partner organizations, and quickly share that content with other users.
-
Automation Analytics runs analytics across multiple Ansible Tower clusters, analyzing usage, uptime, and execution patterns across different teams running Ansible. Users can analyze, aggregate, and report on data around their automation and how that automation is running in their environment.

What you will learn
-
How to use Ansible.
-
As part of the execise, you will call Ansible via an integrated development environment (Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces) and interact with a remote node.
-
-
How to automate a single task on one or many managed nodes (aka ad hoc commands)
-
How to write an Ansible automation blueprint (aka a playbook)
-
How Ansible Automation works with Red Hat’s enterprise Kubernets Platform - OpenShift
-
How to build an OCI container on Red Hat OpenShift via Source-to-Image (S2I)
-
How to use Ansible to provision microservices to a Red Hat Enterprise Linux edge node
-
Lastly, how to configure OS services to update those microservices
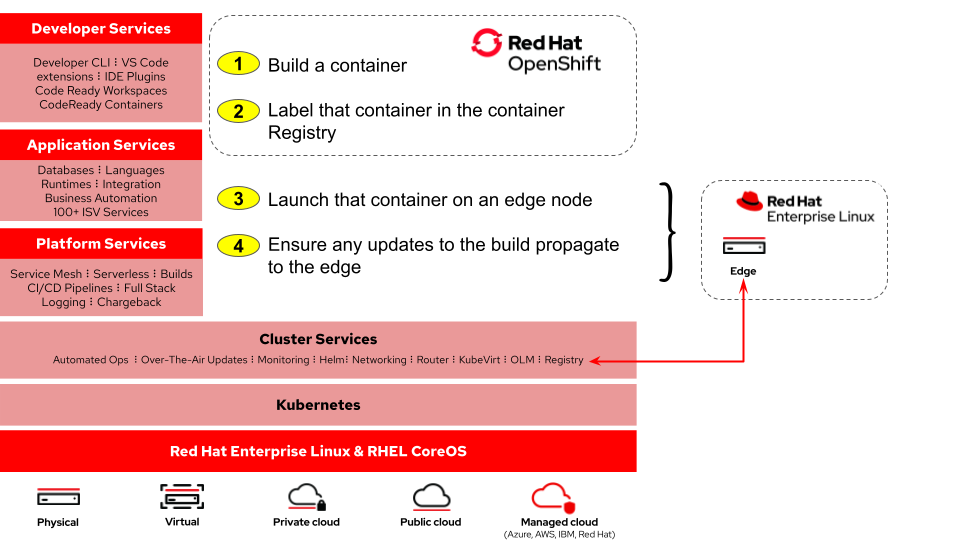
What do we want to do?
(high level)
Where do we start?
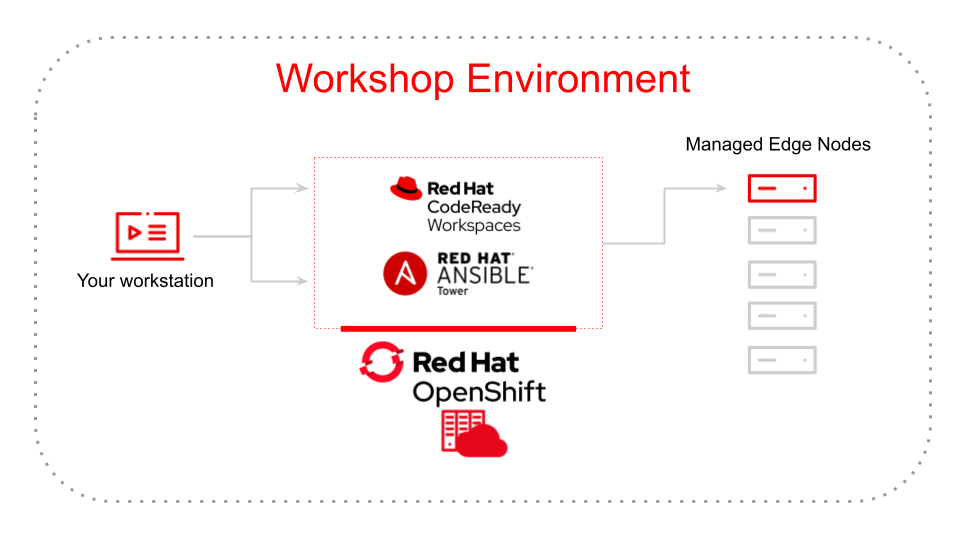
The environment consists of a Red Hat OpenShift cluster running Ansible Automation and Code Ready Workspaces.
As part of the lab, you will …
-
Install skopeo and podman on the Edge node with Ansible Automation Engine
-
Build a container on Red Hat OpenShift (via S2I)
-
On the edge node, we will pull the newly build container and run it with podman through a playbook run on Ansible Tower
-
Configure podman to auto update containers according to their auto-update policy an Ansible workflow
Your Responsibilities
Have a Discussion. This will be boring if it’s just us, up here talking.
Participate. We are going to cut you loose with Ansible, in just a little while. Have questions. Have opinions.
Exercises
Workshop Details
| Domain |

|
|
| Workshop | ||
| Student ID |